DNA test, also called as DNA fingerprinting is done to verify paternity, to find out criminal involvement, in forensic science, in archaeology and other scientific fields. It is a well established fact that DNA fingerprinting test is foolproof. It has its merits in court cases too. It is considered to be a credible evidence of criminal involvement and paternity. Case of N.D Tiwari had also got wide media attention in recent times.
BUT the chances are, you can fail a DNA test even with your real father or mother!
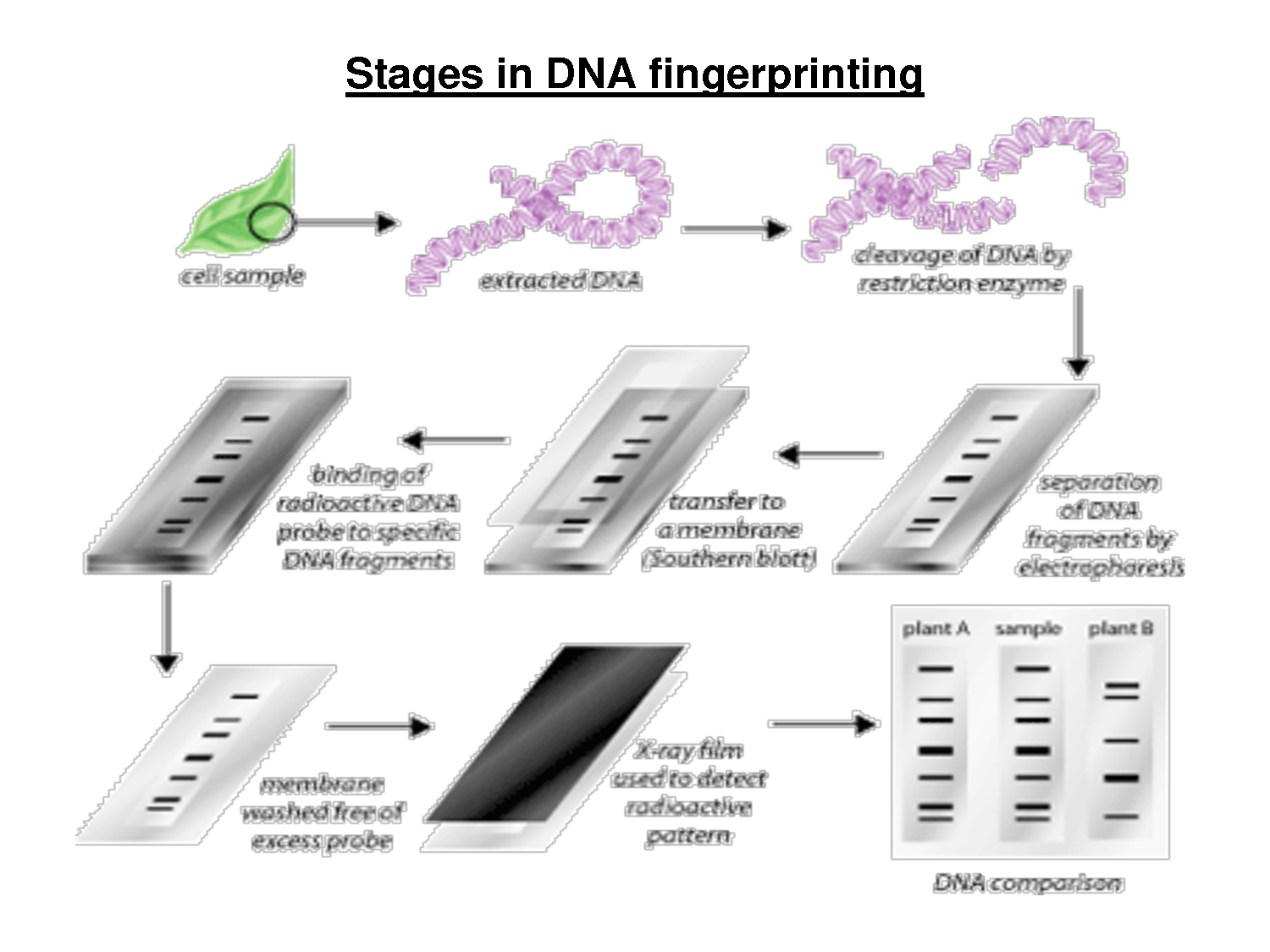
To understand how is it possible, let us look at how DNA Fingerprinting is done.
The technique of DNA fingerprinting/genetic fingerprinting or simply DNA Test was discovered by Dr. Alec Jeffreys in 1984. DNA contain genetic information of an individual. The whole set of genes in an organism is known as Genome. 99.9% of genome is exactly same in every human individual but, 0.1% differs. 0.1% of each individual is unique to the person thus making it possible to identify each individual.
To identify a person by the difference in DNA sequence, the sequence are simply compared to each other. To speed up this process of comparison, rather than each nucleotide, a molecular biologist compares the regions of high variation in DNA sequence, called minisatellites. The location and sequence of minisatellites in genome varies in every individual. The chances of occurrence of same minisatellites are very very low(1 in a billion). Hence it can be treated as unique to every individual just like a fingerprint.
To perform DNA test, the set of DNA is first broken into smaller pieces by an enzyme called restriction endonuclease called Eco R1 which cuts the sequence at distinct location where the sequence is GAATTC or its complementary. The location of of this repetitive sequence varies in every individual. Each fragment is then sorted according to their molecular weight (or size) by a technique called gel electrophoresis.
The fragment are then compared to each other. If the fragments generated by restriction enzymes are of same size it is more likely that both the sequences originated from the same individual. Click here to read more about genetic fingerprinting.
So how can DNA fingerprinting fail?
For the DNA test to fail we have to have two different set of DNA (Genome) in our bodies. It is possible by following ways, This is a concise list for a quick reference.
- Since the human body is a complex and dynamic system, the environmental conditions in different parts of body may lead to changes in DNA, this is a comparatively new idea studied in epigenetics. Though changes occur this way, It is not likely to change the entire DNA and location of microsatellites.
- Transposable elements may also cause the location of some sequence to change. The occurence of transposable elements is not so widespread as to change locations of all microsatellite. Hence, this idea does not seems satisfactory.
- Occurence of more than one kind of cells in terms of genome, in human, i.e Human Chimera was recently seen in a US man who failed the paternity test with his real child.
So what is Human Chimera?
To be simple and precise, human chimera is the occurrence of cells with completely different set of genes in a single individual. It is a very rare condition and may go unnoticed.
Sometimes, when one of the twin dies during early pregnancy, the remnant cell may be taken up and absorbed by the surviving embryo. Thus surviving embryo will have two kinds of genome in different part of the body depending upon the process of differentiation.
Thus, if the cells that form sperm in your body have different set of genome than rest of the cells in your body, you may fail a DNA test! This is a rare condition and chances are low that you would get away with a crime.
If you liked this article or find this article worth reading, please do not forget to share. Who knows, there might be cases of human chimera around you. 🙂
Image Credits:
http://img.docstoccdn.com/thumb/orig/115701763.png