So, today is the great festival of Christmas……! Birthday of The Son of God.. And on this Auspicious day, We want to present before you all the power of Nature… How nature itself provides solution against the problem raised within it….. We all are aware of the epidemics of threat created by Mycobaterium tuberculosis and other related species. But, down here in this article we show how nature provides the solution against it.
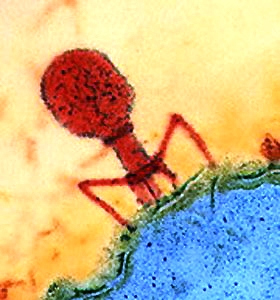
As we know Bacteriophage (Bacterio= Bacteria’s, Phage= eater) infects several bacterium species. In contrast to it, a Mycobacteriophage is a member of a group of bacteriophages that infect mycobacterial species as their hosts e.g., Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis.
The rising incidence of tuberculosis, emergence of multi drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and a slow progress in finding new drugs makes mycobacteriophage a potential candidate for its use as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool against TB.
All the characterized Mycobacteriophages are double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) tailed phages belonging to the order Caudovirales. Most are of the family Siphoviridae , characterized by long flexible non contractile tails, whereas phages of the family Myoviridae, have contractile tails. There is a notable absence of mycobacteriophages from the family Podoviridae (containing short stubby tails), arising the question whether long tails are needed to traverse the relatively thick mycobacterial cell envelope. dsDNA tailed phages are either temperate, forming stable lysogens with a turbid plaque or lytic, forming clear plaques in which the host cells are killed. Mycobacteriophages can also be studied by the morphology of the plaques which vary in size and shape. Plaque morphology also depends on the burst size, which is the number of phage particles released on the lysis of the infected bacteria.

Since the mycobacterial cell wall consists of a mycolic acid rich Mycobacterial outer membrane, attached to an arabinogalactan layer that is in turn linked to the peptidoglycan, it poses significant challenge to the phages. This challenge is met by a set of proteins, namely Lysin B proteins that cleave the linkage of mycolic acids to the arabinogalactan layer, holins that regulate lysis timing, and the endolysins (LysinAs) that hydrolyze peptidoglycan.

Phages affect hosts with a holin-endolysin system essential for programmed lysis. Endolysin is found to be associated with a protein component of the phage tail involved in facilitating the penetration of the murein during injection of the genome into the host. Holins are small membrane proteins that form holes in the membrane through which the endolysin can pass. Holins control the length of the infective cycle for lytic phages so as to achieve lysis at an optimal time.
Endolysins can be a source of potential antibacterial because of its specificity (targeting only a few strains of bacteria) and thus replacing antibiotics (which have a more wide ranging effect), their low probababilty of developing resistance in Mycobacterium and novel mode of action.
Bioinformatics can assist this particular field of research by finding several other proteins existing on this planet or to prepare other such options having similar pharmacophore (physical and chemical attributes) properties. We can demolish the various disease threats by using natural options provided to us and can remain healthy on this planet. The only point to be remembered for this is,
NATURE CAN SATISFY OUR NEEDS, BUT IT CANNOT SUSTAIN OUR GREED….. AS A HEALTHY BODY CONSISTS OF A HEALTHY MIND, THE SAME WAY.. A CONSERVED PLANET CONSERVES ITS SPECIES TOO…..
(A major part of this article consist of some texts copied from
Hatfull, Graham F. “Mycobacteriophages: genes and genomes.” Annual review of microbiology 64 (2010): 331-356.
for any other information related references and queries, please let us know at sanjay@bioinformaticsreview.com