Many a times, we need to visualize and summarize the existing information of the biological sequences like protein or DNA. For this purpose, a new software package has been introduced called ILLUSTRATOR Of BIOLOGICAL SEQUENCE (IBS) which is used for representing the organization of protein or nucleotide sequences in an easy, efficient and precise manner. It visualizes various functional elements. Different features have been provided in IBS such as diagramming of domains,motifs, rescaling, coloring and many more. The standalone packages of IBS were implemented in JAVA, and supported three major Operating Systems, including Windows, Linux and Mac OS.
Key Features:
- the annotations of both protein and nucleotide sequences is supported by the implementation of various drawing elements.
- better color visualization.
- an ‘export module’ is generated with the help of which the final generated artwork can be exported to any publication-quality figure.
- a user-friendly interface.
- various built-in textures enables to color the black-and-white diagrams as per the requirements.
- easy retrieval of UniProt annotations.
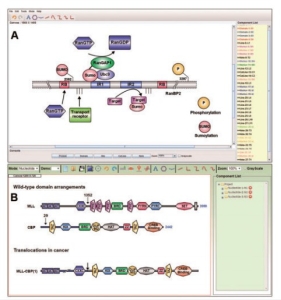
IBS provides individual modes for both proteins and DNA, the protein or DNA sequences can be represented in individual modes. IBS may be proved as a very useful software in many biological researches, for example, with the help of IBS, one can easily diagram the translocations that occur in cancer by parallel view of the wild type arrangements existing in the sequence (as shown in Fig. 1).
“IBS provides an assistance in drawing publication quality diagrams of both protein and nucleotide sequences.”
Fig.1 The main interface of IBS. ( A) The standalone software showing the domain organization of E3 SUMO-protein ligase RanBP2 ( Flotho and Werner,2012).( B) The online service presenting the organization of bromodomain proteins and translocations in cancer.( (Muller et al., 2011 )
Reference:
IBS: an illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences
Wenzhong Liu1,2,†, Yubin Xie1,†, Jiyong Ma1,†, Xiaotong Luo1, Peng Nie1, Zhixiang Zuo3, Urs Lahrmann4, Qi Zhao1, Yueyuan Zheng1, Yong Zhao1, Yu Xue5,* and Jian Ren1,2,3,*