To study macromolecules in homogenous solution, a technique known as SAXS ( Small Angle X-ray Scattering) is used where the obtained scattering patterns are used to design the structure of macromolecules that are proteins, mucleic acids and protein:nucleic acid complexes. In this experiment, a monochromatic X- ray beam is used to illuminate the homogenous solution which forms a scattering pattern. This experiment generates a ab-initio particle shape. This model is compared with the theoretical data available. By comparing the experimental scattering patterns with known scattering data is useful in determination of structure. If the experimental data matches with one or various scattering patterns then it may provide a detailed information about the quarternary and tertiary structure.
DARA is a webserver which initially “computes the scattering profiles from the available structures / models in PDB (Protein Data Bank) and compares these profiles with a given SAXS pattern.” This server is very fast, it compares more than 1,50,000 profiles very rapidly within a few seconds. It almost covers all the models available in PDB. DARA provides good and enhanced results.
How DARA works ?
DARA implements a new search algorithm consisting of principal component analysis and k-d trees for rapid identification of the scattering neighbours, including nucleic acids and complexes.
SAXS data:
For each entry in PDB all biological assemblies are retrieved from the NMR entries whose only first model has considered. The data is represented in the form of curves. The theoretical known scattering curves are obtained by a software i,e., CRYSOL 2.8, which is sufficient to cover models with maximum intra-particle distance Dmax up to 800 A˚. For each model, CRYSOL calculate its Dmax, radius of gyration(Rg), molecular weight (MW) and exclude volume of the hydrated particle (V). For proteins, secondary structure content was computed as the percentage of alpha helices and beta sheets.
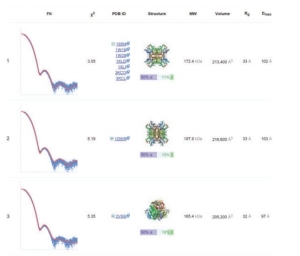
DARA computes various parameters and gives an output which is instantaneous and enhanced. It calculates for almost 100 neighbours of the query macromolecule and the neighbours are ranked according to the best fitting curve are preferred. The result shown in Fig 1 shows the best structures obtained by calculation and comaprison with various parameters considered. The result can also be downloaded.
Fig 1 Top three nearest neighbours for experimental SAXS data collected from glucose isomerase in a phosphate buffer.
DARA represents a quite rapid and easy way to analyze and identify macromolecules in solution which is a difficult process. It can be traced at http://www.embl-hamburg.de/biosaxs/dara.html
Reference:
D A R A : a web server for rapid search of structural neighbours using solution small angle X – ray scattering data
Alexey G. Kikhney1,†, Alejandro Panjkovich1,†, Anna V. Sokolova2 and
Dmitri I. Svergun1,*









![[Tutorial] How to perform docking of zinc metalloproteins using Autodock Vina?](https://bioinformaticsreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/zn.jpg)