A novel coronavirus (CoV), named Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-CoV-2 (SARS-CoV-2) or nCoV-2019, has emerged since December 2019 from Wuhan city of Hubei province in China [1]. This virus belongs to the coronavirus family from which previous outbreaks have emerged (SARS and MERS). They have been a great threat to public health causing many deaths including SARS-CoV-2. There is no proper treatment available to cure this coronavirus disease (covid19). Scientists and researchers are trying really hard to develop a drug or a vaccine or a proper way to cure covid19.
In this essence, Bioinformatics Review has built up a team of worldwide researchers to work on covid19. We will be updating all findings we get during this project. The first study we conducted on SARS-CoV-2 is explained as follows.
Phylogenetics analysis of SARS-CoV-2
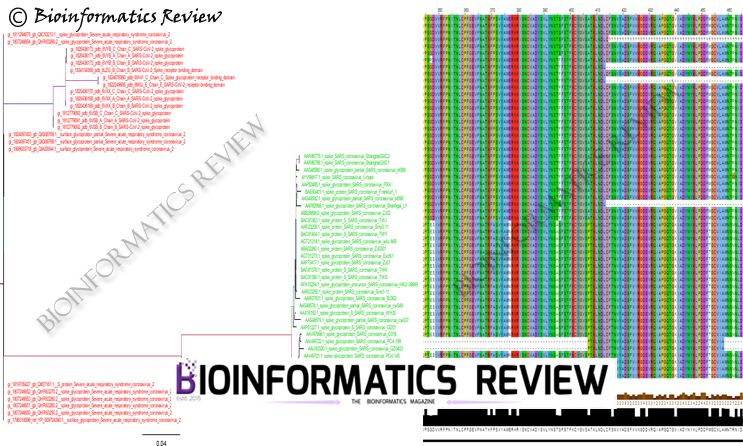
The phylogenetic tree is shown below. This tree was created using the IQTREE tool [2] and the best model was found using ModelFinder [3].
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of SARS-CoV-2 spike sequences with SARS-CoV spike sequences as an outgroup. The red color denotes SARS-CoV-2 spike sequences and green color denotes SARS-CoV spike sequences. The best model was VT+F4 as selected by the ModelFinder and the tree was constructed with 1000 replications.
The branch lengths of spike sequences suggest the divergence of SARS-CoV from SARS-CoV-2. The multiple sequence alignment (MSA) (Fig. 2) of these sequences shows several conserved regions across the entire alignment (File 1).
Further, experiments are being performed for a complete phylogeny and evolutionary study of these sequences. For all updates regarding Covid19 work being done by our research group, visit this page.
References
- Zhu, N., Zhang, D., & Wang, W. China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019 [published January 24, 2020]. N Engl J Med.
- Nguyen, L. T., Schmidt, H. A., Von Haeseler, A., & Minh, B. Q. (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular biology and evolution, 32(1), 268-274.
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B. Q., Wong, T. K., von Haeseler, A., & Jermiin, L. S. (2017). ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature methods, 14(6), 587.