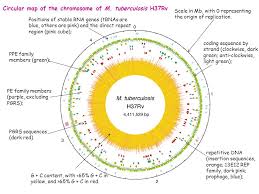
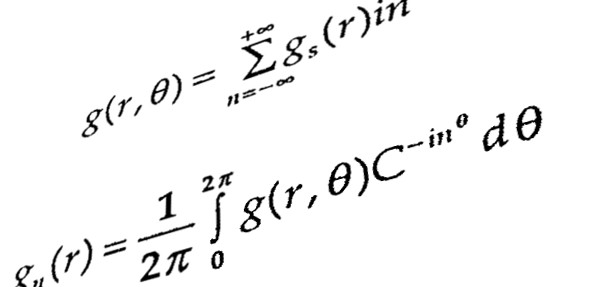Systems biology is not sufficient to full fill the requirement of molecular understanding of any organism at any level. It seeks to contribute multiple approaches and fields to resolve a particular issue arisen from ongoing work. In this article you will find a combinatorial approach of systems biology i.e. molecular, cellular and network biology to understand how tuberculosis is developed and how pathogen succeeds in fighting with host immune systems. A well developed mathematical model, on PhoP-PhoR two component system, is also presented and explained to demonstrate the mode of molecular regulation by pathogen.
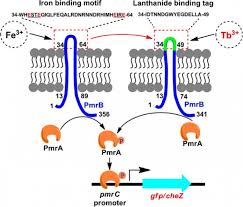
The bacterial two component system (TCS) is a signal transduction system that senses environmental stimuli and responses accordingly. This system consists of two regulating proteins one of which functions as histidine kinase (HK) and other functions as response regulator (RR) in the course of signal cascade mechanism. Mycobacterium tuberculosis have eleven two component systems controlling expression of those genes that are critically involved in the virulence, pathogenicity and survival. Studies have demonstrated that PhoPR-TCS is one of the eleven TCSs peculiarly involved in the virulent activity of the pathogen. PhoPR-TCS is a positive regulator of many genes which encodes gene for the biosynthesis of lipids like sulphatides(SL), diacyltrehalose (DAT) and polycyltrehalose (PAT). These lipid components contribute to the virulency of M. tuberculosis. Studies have corroborated that pks2 and msl3 are responsible for the biosynthesis of SL, DAT and PAT respectively. The expression of these lipid coding genes are regulated by PhoP in association with the autokinase activity of PhoR. In case of Mycobacterial PhoPR TCS, Mg2+ ions have not been substatilally proved to be stimulating factor for PhoR. The simulation of the model was carried out through MATLAB using RK-4 (Runga Kutta fourth order differential equation) method. Resultantly, behavior of TCS was found to be robust at all concentration of Mg2+ ions. The finding can be implicated at the time of development of drug against tuberculosis as to which gene/protein has the high sensitivity towards its stimuli.
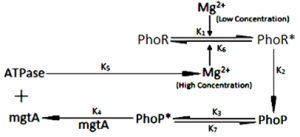
Fig: General presentation of model, depicting feedback mechanism of system
The regulation of TCS is affected by Mg2+ ions to all possible extent which was shown by fluctuations in the level of PhoP and PhoR proteins. The ions have both positive and negative effect over TCS. The result showed that important genes are activated even after ions are switched off from surrounding medium. So, targeting of ions influx and efflux would be of no use in terms of development of drug aginst the pathogen. With some other aspect it can be further tested for more simulations with varying concentration of ions. Since, TCS regulates those genes which are directly involved in pathogenecity and survival of Mycobaterium tuberculosis, understanding the nature and behaiour of individual protein will provide an insight into finding of novel drug target against tuberculosis. The simulation in this work represented the mechanism of gene regulation and its sensitivity twords stimulus and provided the understading about how to deal with when targetting a molecule/protein for any other two component system of the pathogen.