The identification and assignment of functions of unknown macro molecules has been observed to be faster and reliable than the sequence-based methods. This may be due to the structure-based methods which can identify molecules beyond their residues with the help of 3D space.
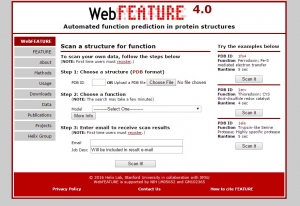
WebFEATURE is a web-based analysis tool for the identification of macro molecules. The users can easily identify the functional sites in the query structures. It scans the query structures beyond the residue identity and also consider the biophysical and biochemical properties of the functional sites in 3D space.
Fig.1 Web interface of WebFEATURE.
The FEATURE system uses a supervised learning algorithm to find the conserved properties from the similar structures and then builds statistical models. These models represents the statistical distribution of physico-chemical properties of the functional sites at distances from the site of interest. It better explains the chemical patterns behind the residues. The supervised learning algorithm automatically discover the physico-chemical properties of the macro molecules.
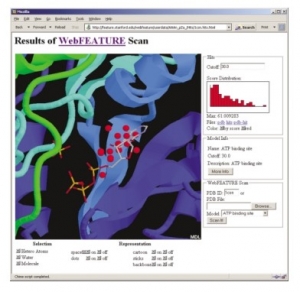
Figure 2. The output of a WebFEATURE scan for an ATP binding site in Casein Kinase-1 (PDB ID: 1csn) shows the hits, above cutoff, superimposed on the structure and crystallographically bound ATP. Hit score statistics are plotted in a histogram to the right of the Chime viewer. By entering a new cutoff in the Cutoff text field, or by clicking on the histogram, the user can change the displayed hits by score. Buttons are provided to change the representation of the molecule and hits. Details on the statistical model are also provided.
The user can also specify the sites and the non-sites in the query structure. Sites are the locations for functional or structural roles and non-sites are those where that function does not occur. The training algorithm generates an output model which differentiates the sites from the non-sites. This generated model is then used as a part of input to the scanning algorithm of FEATURE. The scanning algorithm then analyze the grid points over a query structure for similar sites with in a significant cut-off. The log-odd scoring function of the physico-chemical properties around each grid point is calculated. This score provides a probability (likelihood) that a grid point is a site of interest. The higher the score, more likely the point is of interest.
WebFEATURE is a user-friendly web based tools which also provides offline analysis of the outputs. The result can be downloaded and can be visualized in Chimera, PyMol, etc. The WebFEATURE provides the results in real-time manner.
For further details click here
Note:
An exhaustive list of references for this article is available with the author and is available on personal request, for more details write to muniba@bioinformaticsreview.com.