Tips & Tricks
Careers in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
Bioinformatics is an interesting field of research combining biological sciences and computer sciences. In this article, we will discuss making careers in bioinformatics for starters.
Making a career in bioinformatics is not a difficult task as it sounds unless you are seeking it without interest. Bioinformatics is being widely used in biological research these days. You can look for a job in the private sector or academics. Wages depend upon the education, job sector, and experience.
What do bioinformaticians do?
Basically, bioinformaticians solve biological problems by applying computer science techniques and methods. They develop several software, tools, and also possess expertise in analyzing the outputs of the software. A detailed article has been published previously explaining the roles of bioinformaticians/bioinformaticists.
Bioinformatics researchers try to answer scientific questions by doing experiments in silico with available software or by developing new ones. They explore different programs and/or develop new ones if needed and apply them to solve real-world problems.
What bioinformatics research include?
Generally, bioinformatics researchers ask questions such as
- “What is a methodology to find/design a drug for a particular disease?”
- “In order to study the complete evolutionary history of an organism or a genus, what tools must be used?”
- “If required software/tools are not available then how to develop one?”
- “How can we find new ways to reduce computing time?”
Basic research in bioinformatics includes the following tasks:
- designing experiments and methodologies.
- writing proposals to get research grant or approval for projects.
- conducting experiments in silico
- analyzing data
- writing papers, publishing them in reputed scientific journals, and presenting at scientific conferences.
Jobs in bioinformatics involve research work in a company (private sector), or government organizations and agencies, universities, colleges, and non-profit organizations. Bioinformatics job titles include Research Assistant, Research Associate, research scientist. At higher levels such as assistant professor, associate professor, a professor (in colleges and universities), lead scientist (private company), and principal investigator (government labs, or non-profit organizations), bioinformatics researchers have an added responsibility of managing a lab or a research group and postdoctoral fellows.
Teaching in this area include managing classes, preparing lectures according to the syllabus, teaching classes along with managing a lab, grading and writing exams, and advising students. At college and university level, professors direct a lab and do research work along with teaching classes, whereas lecturers only teach.
How to prepare for a career in bioinformatics?
It depends on at what level of education you are right now. If you are in high school, then it would be a good start to choose subjects wisely including biology and informatics practices. However, you can always learn bioinformatics and computational biology if you have an interest in it. It doesn’t matter whether you have a biology or computational background or not, however, you might need to work hard.
Here are some books mentioned in this article that will help you to get started on learning bioinformatics. Following is a table showing different activities you need to focus on at different levels of education. Further, it always requires a Ph.D. degree to work on high posts in colleges and universities. Post Ph.D., researchers choose to work as postdoctoral research associates for additional experience.
| Senior Secondary | Undergraduate | Masters |
| Informatics Practices | Life Sciences | Bioinformatics |
| Biology | Focus on Bioinformatics | Object-Oriented Programming |
| Mathematics (optional) | Biological Databases | Python, Perl, R |
| HTML, C/C++ | Software usage | Java, PHP, MySQLi, NoSQL |
| Oracle/SQL | Basic programming- C/C++ | |
| Visual Basic |
In the field of bioinformatics, it is always good to learn advanced programming languages, especially object-oriented programming. It will help you develop new software and tools as per the requirements of the biological problems. Besides, participate in some workshops and seminars/conferences that will help you develop technical, communication, and leadership skills.
Further Reading
Tips & Tricks
Common mistakes made during computational docking.

Computational docking is not a trivial task once we avoid making some mistakes. In this section, let’s learn about some important points that we should keep in mind while performing computational docking.
Tips & Tricks
How to download FASTA sequences from PDB for multiple structures?

In this article, we are going to download FASTA sequences for multiple structures from PDB [1]. We need to have PDB IDs only for input. (more…)
Software
How to install the LigAlign plugin on Pymol on Ubuntu (Linux)?

Few errors appear when we try to run the LigAlign plugin [1] in Pymol [2]. For example, if you try to run the ligand_alignment plugin, it will give you multiple errors including “Unable to initialize LigAlign v1.00“, or “can’t run LigAlign v1.00” or “incorrect Python syntax” or “Plugin has been installed but initialization failed“. In this article, we explain the reason for this issue and how you can rectify these errors. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
How to make an impactful science presentation?
After your hard work, it is time to showcase your study and the methods of your study to an audience. You must make every point useful and informative. Here, in this article, we are going to share some tips to make your scientific presentation impactful. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
Basic bioinformatics concepts to learn for beginners
This article is for beginners who are stepping into the field of bioinformatics. We will discuss some basic concepts that you need to learn while trying to enter the field of bioinformatics. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
A Beginner’s Guide on How to Write Good Manuscripts

Drafting a manuscript could be a difficult task for beginners in the field of research. In this article, we will provide a few tips for how can you write a good manuscript being a research scholar. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
How to remove HETATMS and chains from PDB file?

This is a basic tutorial on removing the hetero-atoms (HETATMS) and chains from PDB files. It is an essential step for computational and molecular dynamics simulation. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
Importance of Reasoning in Research

Research is considered complicated. As it involves reading multiple research articles and reviews, devising hypotheses and appropriate experiments, and last but not the least, getting a significant output. This seems difficult to read multiple research papers and then extract useful information regarding your project. It involves a methodology to read and understand research articles in one go. This is explained in our previous article “A guide on how to read the research articles”. This article explains the importance of thinking during your entire research. (more…)
Docking
How to Find Binding Pocket/ Binding Site for Docking?
Finding binding sites/pockets in a target protein is one of the important steps in docking studies. It is relatively easier to find a binding pocket in the proteins whose resolved structures are available in PDB than that of the predicted structures. In this article, we will discuss the ways to know a binding pocket or a binding site in a target protein. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
Current Research Topics in Bioinformatics

Researchers working in the scientific area always want to explore new and hot topics to make informed choices. In this article, all new, current, and demanding research topics in bioinformatics are mentioned. This article is helpful for the researchers who are looking for trends in bioinformatics to select a research topic of broad-spectrum. (more…)
MD Simulation
MD Simulation using GROMACS: Things to remember
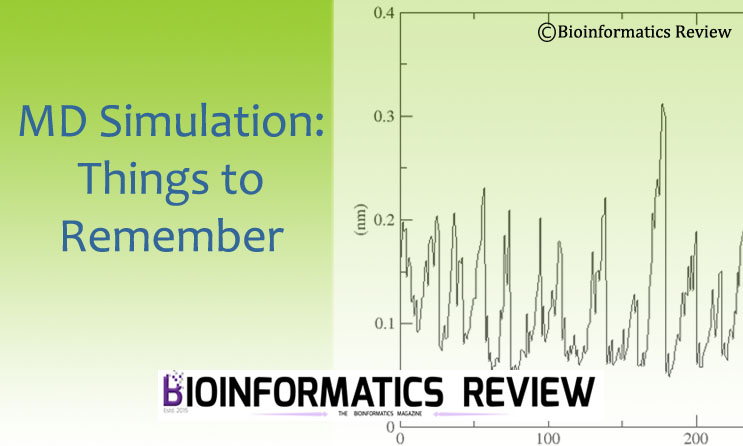
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is considered amongst the important methods in bioinformatics. Installation of MD simulation software and execution of their commands is critical. It requires several parameters to be considered before performing simulations. A single mistake may result in impractical outputs. In this article, we will discuss such important things to remember during the MD simulation and installation and execution of its software (GROMACS) [1,2]. (more…)
Bioinformatics Books
List of Bioinformatics Books for Beginners
It is difficult to decide which book to read to start learning bioinformatics. Beginners can read this article to know the basic steps involved in learning bioinformatics. A few books are suggested in this article to read for starters in bioinformatics. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
Bioinformatics- Where & How to Start?
Bioinformatics being an interdisciplinary area of biological science and computer science may sound complicated to beginners in this field. However, it is quite simple. The only thing you need is knowledge in both areas. Here is a way for the beginners to start with bioinformatics. (more…)
Docking
Common mistakes made during Autodock Vina Installation and Execution

Several errors occur while installing MGLTools and Autodock Vina on Ubuntu. We have explained the complete process of Autodock Vina installation and docking in previous articles. Here are some common errors and mistakes that should be taken care of while installing and running Vina on Ubuntu. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
What does a bioinformatician do?
Bioinformaticians play an important part in data analysis and result interpretation in the field of bioinformatics. However, it is unclear to many what specific role bioinformaticians play day to day. We are often asked by many about what exactly a bioinformatician does. But first, who is a bioinformatician?
Software
MGL Tools & Autodock Vina installation: Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
I have received several e-mails from researchers and students alike regarding installing MGL Tools and Autodock Vina on Ubuntu. Most questions are similar in nature, so I thought of answering them once and for all. In this article, I have collected some frequently asked questions and provided the link to their answers in our question-answer section of Bioinformatics Review. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
A guide on how to read the research articles
Reading a research article could be a problem for students starting their careers in research. Research papers are sometimes difficult to understand especially when you are new to this field. In this article, we will discuss how to read and understand a research article. (more…)
Tips & Tricks
Bioinformatics and programming languages- what do you need to know!
There are various things which come to mind when someone is going to enter in the field of Bioinformatics and the topmost concern is “Do I need to learn computer languages to pursue my career in Bioinformatics?”. The answer is a bit tricky but it could be both “yes” and “no”. This article will describe the conditions where you need to learn programming languages in Bioinformatics. (more…)
Docking
Site-specific docking: Frequently Asked Questions & answers for starters
I have been getting several E-mails from researchers and students alike regarding in-silico docking. Most questions are similar in nature, so I thought of answering them once and for all. In this article, I have collected some frequently asked questions and provided the link to their answers present in our question-answer section of Bioinformatics Review.
It is good to have questions in mind and they can be solved in a way as quoted by Sir Einstein:
“We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them.”
In this article, I have collected some of the most Frequently Asked Questions while performing site-specific and/ or blind docking. You have to consider a lot of factors before performing an actual docking on a protein with a specific ligand.
Question: How do you predict protein’s binding sites?
Question: What is the difference between the blind docking and binding site based docking?
Tips & Tricks
Survival guide: How to overcome lab politics and not become a lab rat

If you find yourself in a laboratory full of people with scientific temperament, it can be exciting, awesome and hilarious. You may experience a real life “big bang theory” episode and witness all characters around you.
However, for the uninitiated, a large number of labs are a flourishing ground of rivalry and war grounds reiterating the fact on its inhabitant that they live in a maze.
Lab politics can be nasty, and those who don’t want to get involved are almost certainly the easiest target.
Here are a few tips based on my experience in labs on how to survive lab politics and prevent yourself from getting into situations uncalled for.
- Communicate Backbiting and misinformation is the nuclear weapon of every mole. They pass on false information about you leading to complexities. It ranges from simple misinformation about you being absent or drunk during work hours when you are not, to some complicated statements attributed to you. You can deal with this situation through regular communication. with your peers. Every one of them. Especially if you sense that your guide is growing weary of you. communicate as clearly as possible and if you sense misinformation, make it a priority to point it out without targeting the person acting as a mole. This will be such a blow…..oops!
- Be Humble
Back in my graduation days, I was made a leader for a group project, I worked harder than everybody suddenly realizes that it was only me that was working for the whole duration. So I became proud which reflected in my behavior. Seeing this, two girls approached the guide with some story, which I am still unaware of. The guide, who happens to be a lady, immediately removed me from the project & my name from the manuscript after it completed. The results were published without my name, the first author being that girl who was not even fully aware of the topic. Moral? even if you are doing everything, be humble or you risk being a lab rat.
- Divert to productivity
When somebody else is the target, it is relatively easy for you to just ignore what is happening but remaining silent in such situations will lead to an exponential increase in it and you never know when the dial points at you. You may try shifting focus to an interesting observation, experiment, or paper. This way, you show them that what these guys are talking about is not worth the time. - Don’t be evil If someone is doing something a certain way and you know they are wrong, just point it to them. Don’t go to your guide to complain. If you complain too much it is perceived as a negative trait. If you have problems try to resolve them on your own rather than asking someone to do them for you. If you can’t do it yourself, try to get help rather than ordering. Nobody owes you anything so be humble.
- Don’t over-promise
You may become a target without even saying a word! yes! it happens. The world is full of hatred for achievers. So if you have a lot in your kitty, don’t keep flaunting it. don’t promise that you will do this and that. Just keep doing things one by one. So they won’t even notice that you were running your own race and they were not even the participants.
6. Don’t get discouraged
If you are surrounded by ‘lab politicians’ and they criticize your work and working habits, then don’t get discouraged, because they would be trying to distract you from your work. In fact, it is a good sign, great success comes with criticism. Don’t believe what they say because ‘politicians’ never want anyone else’s account to be filled, just say thanks to them with a smile and keep going in your direction.
These are the tips that I have learned by working at labs in the University of Delhi, Indian Institute of Science Education & Research – Kolkata, Jamia Millia Islamia & Jawaharlal Nehru University.
Although I have tried to accommodate as much as I could, do you think I have missed something? would like to add something to the story? go ahead and comment below.



You must be logged in to post a comment Login