Algorithms
MOCCA- A New Suite to Model cis- regulatory Elements for Motif Occurrence Combinatorics
cis-regulatory elements are DNA sequence segments that regulate gene expression. cis-regulatory elements consist of some regions such as promoters, enhancers, and so on. These regions consist of specific sequence motifs.
A newly expanded suite is developed to model the motif occurrence combinatorics in DNA sequences [1]. This suite is known as MOCCA (Motif Occurrence Combinatorics Algorithms). It is based on support vector machines (SVM) and random forest (RF) models, SVM-MOCCA and RF-MOCCA respectively.
Users enter motifs, training sequences, and model specifications. The sequences are provided in FATSA format or can be generated by either an i.i.d. model or an N-th order Markov chain. Users can enter IUPAC nucleotide code motifs and Position Weight Matrix (PWM) motifs.
MOCCA implements three types of models:
- CPREdictor
- Dummy PREdictor
- SVM-MOCCA
- including a new hierarchical model RF-MOCCA.
MOCCA is implemented in C++ with a minimal number of dependencies to ease the process of installation. It can be installed on Unix-based systems.
MOCCA is freely available to download from Github.
For more details, read here.
References
- Bredesen, B.A., Rehmsmeier, M. (2021). MOCCA: a flexible suite for modelling DNA sequence motif occurrence combinatorics. BMC Bioinformatics 22, 234.
Algorithms
vs_Analysis.py: A Python Script to Analyze Virtual Screening Results of Autodock Vina

The output files obtained as a result of virtual screening (VS) using Autodock Vina may be large in number. It is difficult or quite impossible to analyze them manually. Therefore, we are providing a Python script to fetch top results (i.e., compounds showing low binding affinities). (more…)
Algorithms
How to search motif pattern in FASTA sequences using Perl hash?

Here is a simple Perl script to search for motif patterns in a large FASTA file with multiple sequences.
Algorithms
How to read fasta sequences from a file using PHP?
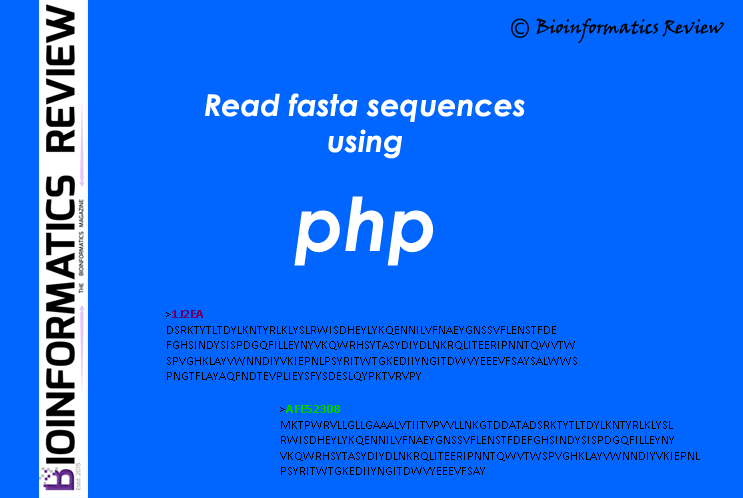
Here is a simple function in PHP to read fasta sequences from a file. (more…)
Algorithms
How to read fasta sequences as hash using perl?
This is a simple Perl script to read a multifasta file as a hash. (more…)
Algorithms
BETSY: A new backward-chaining expert system for automated development of pipelines in Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics analyses have become long and difficult as it involves a large number of steps implemented for data processing. Bioinformatics pipelines are developed to make this process easier, which on one hand automate a specific analysis, while on the other hand, are still limited for investigative analyses requiring changes to the parameters used in the process. (more…)
Algorithms
Algorithm and workflow of miRDB
As mentioned in the previous article, Micro RNAs (miRNAs) are the short endogenous RNAs (~22 nucleotides) and originate from the non-coding RNAs [1], produced in single-celled eukaryotes, viruses, plants, and animals [2]. They play significant roles in various biological processes such as degradation of mRNA [3]. Several databases exist storing a large amount of information about miRNAs, one of such databases miRBase [4] was explained in the previous article, today we will explain the algorithm of miRDB [5,6], another database for miRNA target prediction. (more…)
Algorithms
miRBase: Explained
Micro RNAs (miRNAs) are the short endogenous RNAs (~22 nucleotides) and originate from the non-coding RNAs [1], produced in single-celled eukaryotes, viruses, plants, and animals [2]. miRNAs are capable of controlling homeostasis [2] and play significant roles in various biological processes such as degradation of mRNA and post-translational inhibition through complementary base pairing [3]. (more…)
Algorithms
Prediction of biochemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes in humans
There are many biological important enzymes which exist in the human body, one of them is Cytochrome P450 (CyP450) enzymes which are mostly considered in drug discovery due to their involvement in the majority (75%) of drug metabolism [1]. Therefore, various in-silico methods have been applied to predict the possible substrates of CyP 450 enzymes [2-4]. Recently, an in-silico model has been developed to predict the potential chemical reactions mediated by the enzymes present in humans including CyP450 enzymes [5]. (more…)
Algorithms
A new high-level Python interface for MD simulation using GROMACS
The roots of the molecular simulation application can be traced back to physics where it was applied to simplified hard-sphere systems [1]. This field of molecular simulation study has gained a lot of interest since then and applied to perform simulations to fold small protein at multi-microsecond scale [2-4], predict functional properties of receptors and to capture the intermediate transitions of the complex [5], and to study the movement and behavior of ligand in a binding pocket and also to predict interactions between receptors and ligands [6,7]. (more…)
Algorithms
Machine learning in prediction of ageing-related genes/proteins
Ageing has a great impact on human health, when people’s age advance towards 80 years, approximately half of the proteins in the body get damaged through oxidation. The chemical degradations occurring in our body produce energy by the consumed food via oxidation in the presence of oxygen. (more…)
Algorithms
Simulated sequence alignment software: An alternative to MSA benchmarks

In our previous article, we discussed different multiple sequence alignment (MSA) benchmarks to compare and assess the available MSA programs. However, since the last decade, several sequence simulation software have been introduced and are gaining more interest. In this article, we will be discussing various sequence simulating software being used as alternatives to MSA benchmarks. (more…)
Algorithms
Benchmark databases for multiple sequence alignment: An overview
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is a very crucial step in most of the molecular analyses and evolutionary studies. Many MSA programs have been developed so far based on different approaches which attempt to provide optimal alignment with high accuracy. Basic algorithms employed to develop MSA programs include progressive algorithm [1], iterative-based [2], and consistency-based algorithm [3]. Some of the programs incorporate several other methods into the process of creating an optimal alignment such as M-COFFEE [4] and PCMA [5]. (more…)
Algorithms
ab-initio prediction of protein structure: An introduction

We have heard a lot about the ab-initio term in Bioinformatics, which could be difficult to understand for newbies in the field of bioinformatics. Today, we will discuss in detail what ab-initio is and what are the applicable methods for it. (more…)
Algorithms
Intrinsically disordered proteins’ predictors and databases: An overview
Intrinsically unstructured proteins (IUPs) are the natively unfolded proteins which must be unfolded or disordered in order to perform their functions. They are commonly referred to as intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) and play significant roles in regulating and signaling biological networks [1]. IDPs are also involved in the assembly of signaling complexes and in the dynamic self-assembly of membrane-less nuclear and cytoplasmic organelles [1]. The disordered regions in a protein can be highly conserved among the species in respect of both the composition and the sequence [2]. (more…)
Algorithms
An introduction to the predictors of pathogenic point mutations

Single nucleotide variation is a change in a single nucleotide in a sequence irrespective of the frequency of the variation. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) play a very important role in causing several diseases such as the tumor, cancer, etc. Many efforts have been made to identify the SNVs which were initially based on identifying non-synonymous mutations in coding regions of the genomes. (more…)
Algorithms
SparkBLAST: Introduction

The basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) [1,2] is known for its speed and results, which is also a primary step in sequence analysis. The ever-increasing demand for processing huge amount of genomic data has led to the development of new scalable and highly efficient computational tools/algorithms. For example, MapReduce is the most widely accepted framework which supports design patterns representing general reusable solutions to some problems including biological assembly [3] and is highly efficient to handle large datasets running over hundreds to thousands of processing nodes [4]. But the implementation frameworks of MapReduce (such as Hadoop) limits its capability to process smaller data. (more…)
Algorithms
Role of Information Theory, Chaos Theory, and Linear Algebra and Statistics in the development of alignment-free sequence analysis

Sequence alignment is customary to not only find similar regions among a pair of sequences but also to study the structural, functional and evolutionary relationship between organisms. Many tools have been discovered to achieve the goal of alignment of a pair of sequences, separately for nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence, BLOSSUM & PAM [1] are a few to name. (more…)
Algorithms
Bioinformatics Challenges and Advances in RNA interference

RNA interference is a post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism to down-regulate the gene expression either by mRNA degradation or by mRNA translation inhibition. The mechanism involves a small partially complementary RNA against the target gene. To perform the action, it also requires a class of dedicated proteins to process these primary RNAs into mature microRNAs. The guide sequence determines the specificity of the miRNA. Therefore, the knowledge of the guide sequence is crucial for predicting its targets and also exploiting the sequence to create a new regulatory circuit. In this short review, we will briefly discuss the role and challenges in miRNA research for unveiling the target prediction by bioinformatics and to foster our understanding and applications of RNA interference. (more…)
Algorithms
Systems pharmacology and drug development

Systems pharmacology is an emerging area in the field of medicinal chemistry and pharmacology which utilizes systems network to understand drug action at the organ and organism level. It applies the computational and experimental systems biology approaches to pharmacology, which includes network analyzes at multiple biological organization levels facilitating the understanding of both therapeutic and adverse effects of the drugs. Nearly a decade ago, the term systems pharmacology was used to define the drug action in a specific organ system such as reproductive pharmacology [1], but to date, it has been expanded to different organ and organism levels [2]. (more…)
Algorithms
Recent advances in in-silico approaches for enzyme engineering
Enzymes are natural biocatalysts and an attractive alternative to chemicals providing improved efficiency for biochemical reactions. They are widely utilized in industrial biotechnology and biocatalysis to introduce new functionalities and enhance the production of enzymes. In order to be proved beneficial for industrial purposes, the enzymes need to be optimized by applying protein engineering. This article specifically reviews the recent advancements in the computational approaches for enzyme engineering and structural determination of the enzymes developed in recent years to improve the efficiency of enzymes, and the creation of novel functionalities to obtain
products with high added value for industrial applications. (more…)




You must be logged in to post a comment Login